Table of Contents
A rectifier is a device that changes alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It uses special parts called semiconductor diodes to do this. There are different types of rectifiers including half wave, full wave and full wave bridge rectifiers. Before you talk about how rectifiers are used, let us quickly go over what they are.
Unregulated & Regulated Rectifiers
There are two types of DC rectifier applications which are unregulated and regulated.
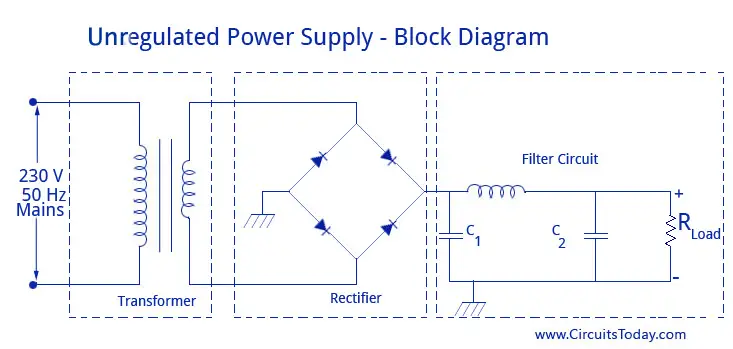
Unregulated rectifiers are a cost-effective way to get a lot of DC power. They have a transformer that changes the incoming voltage and silicon diodes that turn AC power into DC power.
Regulated rectifiers are a bit more complex. They use a special device called a thyristor (or SCR) to control how much voltage or current goes to the load.
Both unregulated and regulated DC rectifier applications have many features and options to help you get the exact DC power you need.
Components
Transformer
- Dry Type Transformer
The dry type transformer changes the incoming voltage to the voltage needed for the rectifier. It has special insulation that can handle temperatures up to 220°C. The transformer uses very pure copper or aluminum for its coils. The coils are treated under vacuum with a special varnish to keep them sturdy. They are built to be strong and can handle short circuits well. The core is made from a high-quality, low-loss material called M6 silicon steel. This transformer also has two settings to adjust the voltage slightly higher or lower which make it easier to match the incoming AC line voltage. There are also water-cooled options available.
- Transformer — Liquid Filled
Liquid-filled transformers are filled with mineral oil and can handle a temperature rise of 65°C. They use either copper or aluminum wire and come in sizes from 1000 KVA to about 10 MVA. They meet important ANSI standards. There are also some extra options available like:
-
- Stainless Steel Tank
-
- Lightning Arrestors
-
- Load Tap Changer
-
- Oil Preservation System
-
- Fans with Control Transformer
-
- Primary/Secondary Electrostatic Shielding
-
- Primary/Secondary Bushings
-
- Grounding Resistors
-
- Liquid Level Gauge
-
- Liquid Temperature Gauge
-
- Pressure/Vacuum Regulator
-
- Pressure Relief Device with Indication
-
- Silicone Filled
-
- Drain Valve with Sampling Device
- High Voltage Transformers
There are also transformers for high voltage applications. Usually, these systems need another transformer to lower the incoming voltage before connecting to the rectifier-transformer. Benoit Technologies make high voltage transformers which means you will not need to buy that extra transformer because it is already built into the rectifier system. This helps save money.
Specifications
Unregulated Rectifiers
- Silicon Diodes
Silicon diodes change AC power into DC power. They let electricity flow in one direction but block it from going the other way. Hermetically sealed diodes are completely protected from outside conditions thus they can work in tough environments and handle high temperatures. Surge suppression networks help keep the reverse voltage on the diodes within a safe limit which make sure it does not exceed three times the rated DC voltage. Diodes can be attached to heatsinks that are either cooled by air or water.
- Input Voltage
230/460 Volts AC (high input voltages are also available).
- Output Voltage
Up to 600 Volts DC (other output voltages available upon request).
- Output Current
Through 30,000 Amperes (other output currents available upon request).
- Power Factor
96% or greater from 25% to 100% at rated voltage.
- Ripple
4.5% RMS AC ripple maximum at rated voltage and current.
- Efficiency
96% at full load with rated input voltage.
Source: circuitstoday.com
Specifications
Regulated Rectifiers
- Thyristors (SCRs)
Thyristors which is also known as SCRs help control the voltage or current in a circuit. They can be found either before or after a transformer. Thyristors start working at a certain point in the positive part of the AC wave. This allows us to manage how much voltage or current goes to the load.
- Primary Regulation
In primary regulated systems, special electronic switches called thyristors are placed between the incoming electricity source and the transformer. This setup helps control how much voltage goes to the transformer. To manage both the positive and negative parts of the electricity cycle, two thyristors are connected together for each phase. Thyristors work well with high voltage and low current which means they are helpful on the primary side of the transformer where the current is lower. This design leads to a smaller, more efficient DC power supply for industries that costs less to make. The controlled AC voltage is then sent to an isolation transformer which lowers the voltage before sending it to diodes that convert it to direct current (rectification).
- Secondary Regulation
A rectifier can control voltage or current after a transformer. Instead of diodes, it uses thyristors to change and regulate power. This setup is common in high voltage systems to protect against sudden voltage changes and noise. Thyristors can be cooled by air or water to manage heat.
- Silicon Diodes
In a primary regulated system, silicon diodes let electricity flow in one direction only. Sealed diodes are protected from bad conditions and can handle high temperatures. Surge protection keeps the reverse voltage safe which ensure it is at least three times higher than the diode’s normal working voltage.
- Input Voltage
230/460 Volts AC (high input voltages are also available).
- Output Voltage
Up to 600 Volts DC (other output voltages available upon request).
- Output Current
Through 30,000 Amperes (other output currents available upon request).
- Power Factor
Typically better than 90% when operating near full rated output.
- Ripple
4.5% RMS AC ripple maximum at rated voltage or current.
- Efficiency
Typically better than 95% at full load; with rated input voltage, typically between 96-97%.
Conclusion
DC rectifiers in manufacturing companies play a vital role in various industrial applications by converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This process is essential for powering many devices including motors, batteries and electronic equipment. Industries such as manufacturing and telecommunications rely on DC rectifiers for their efficiency and reliability. By ensuring a steady flow of electricity, rectifiers help improve the performance and safety of machinery.
You can approach Benoit Technologies who helps manage data center projects for technology, backup power and data services. We have a lot of experience and can design, buy, set up and start IT projects for you. When you work with us, we take care of the contractors and vendors and keep you updated so you can relax. We also have the right products to offer you the best solutions.



